A family owned business providing a full range of home health and school nursing services
Why Blood Sugar Control Is Critical for Effective Wound Healing in Diabetic Patients
Managing Wounds with Diabetes
Managing wounds with diabetes requires an understanding of how the condition disrupts the body’s natural healing process. Wound healing occurs in four distinct stages:
- Hemostasis: Blood clotting to stop bleeding.
- Inflammation: Immune cells prevent infection.
- Proliferation: New tissue and blood vessels form.
- Remodeling: The tissue strengthens and restores.
One of the most significant impacts of diabetes is its effect on circulation. High blood sugar damages blood vessels, restricting the flow of oxygen and nutrients that are essential for repairing tissue. This limitation delays the healing process and increases the risk of complications, such as infections that can quickly become severe.
Nerve damage, or neuropathy, is another common complication of diabetes that can significantly hinder wound management. Neuropathy often reduces sensation in the extremities, particularly the feet, making it difficult for patients to notice injuries. Without prompt treatment, these unnoticed wounds can worsen, leading to chronic infections or, in extreme cases, amputations.
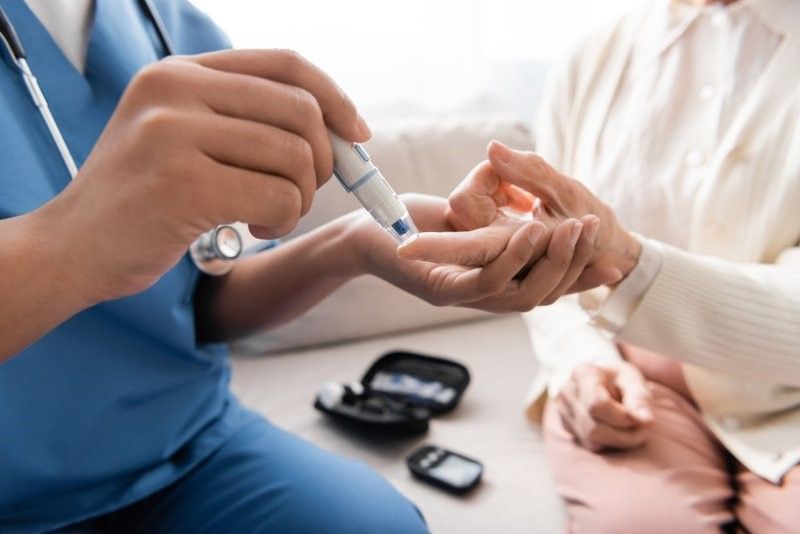
The Role of Blood Sugar in Wound Healing
High glucose levels weaken the immune system, reducing its ability to fight infections effectively. This prolongs healing and increases the risk of complications like abscesses or systemic infections.
Another challenge is impaired collagen production. Collagen is critical for wound strength and tissue repair, and when glucose levels are elevated, collagen synthesis slows, leading to chronic wounds that take much longer to heal.
Additionally, elevated glucose contributes to the formation of advanced glycation end products (AGEs), compounds that damage proteins and cells. AGEs:
- Impair collagen function.
- Increase oxidative stress, damaging cells.
- Promote chronic inflammation, further delaying healing.
This vicious cycle of inflammation and tissue damage underscores the importance of maintaining stable blood sugar levels for effective wound healing.
Strategies for Managing Wounds with Diabetes
For diabetic patients, blood sugar management is at the heart of effective wound care. Consistent monitoring of glucose levels helps ensure that the body remains in an optimal state for healing. This proactive approach allows patients to make necessary adjustments to their diet, medications, and lifestyle to maintain stable blood sugar levels.
A balanced diet plays a crucial role in managing wounds with diabetes. Foods rich in vitamins and minerals support the body’s healing processes, while avoiding high-sugar foods helps prevent spikes in glucose levels. Staying hydrated is equally important, as dehydration can exacerbate circulation issues and slow wound healing.
Incorporating physical activity, where possible, also promotes circulation and helps regulate blood sugar. Even moderate, low-impact exercises, such as walking, can improve overall health and create a supportive environment for healing.
Collaboration between patients and healthcare providers is essential for effective wound management. This team-based approach often includes tailored treatment plans that address both blood sugar control and wound care. Interventions may include medication adjustments, wound-cleaning techniques, and education on how to prevent future injuries. By addressing both immediate needs and long-term management, patients are better equipped to heal and reduce the risk of recurring wounds.
At-Home Support for Diabetic Wound Care
Many diabetic patients benefit from specialized at-home wound care services that bring expert support directly to them. Managing wounds with diabetes can feel overwhelming, especially when balancing daily responsibilities. At-home care simplifies this process by offering personalized solutions that address the unique needs of each patient.
One of the key advantages of at-home care is the emphasis on patient education. Understanding the connection between blood sugar and wound healing enables patients to make informed decisions about their health. This knowledge fosters better adherence to treatment plans and encourages proactive management of both diabetes and wound care.

Preventing Complications and Future Wounds
Managing wounds with diabetes is about healing current injuries and preventing new ones. Prevention strategies focus on addressing the root causes of chronic wounds and minimizing risk factors. For example, regular foot inspections are vital for identifying small injuries before they become serious. Diabetes-related neuropathy often masks the pain or discomfort that would normally alert a person to a wound, making daily checks an essential habit.
Proper footwear is another crucial factor in prevention. Shoes that fit well and provide adequate support can prevent blisters, calluses, and other minor injuries that might otherwise go unnoticed. Maintaining overall health by managing related conditions, such as high blood pressure or high cholesterol, further supports the body’s ability to heal and reduces the risk of complications.
Taking Action to Support Healing
For diabetic patients, the connection between blood sugar control and wound healing is clear. By managing glucose levels, they can significantly improve their body’s ability to recover, reduce the risk of infections, and avoid complications that could lead to chronic wounds or amputations. The journey to recovery requires both commitment and support, and no one has to face it alone.
CritiCare’s at-home diabetic wound care services are designed to provide that crucial support. Through tailored care plans, patient education, and a focus on blood sugar management, CritiCare helps patients navigate the challenges of wound healing with confidence and ease. Contact us today to learn more.

CONTACT INFORMATION
Chadds Ford PA 19317
info@criticareplus.com
Mon-Fri 9:00 AM - 5:00 PM, Sat-Sun - Closed
24 Hours on call services
OUR LOCATION
BROWSE
CONTACT INFORMATION
Chadds Ford PA 19317
info@criticareplus.com
Mon-Fri 9:00 AM - 5:00 PM, Sat-Sun - Closed
24 Hours on call services
OUR LOCATION










